
[ad_1]
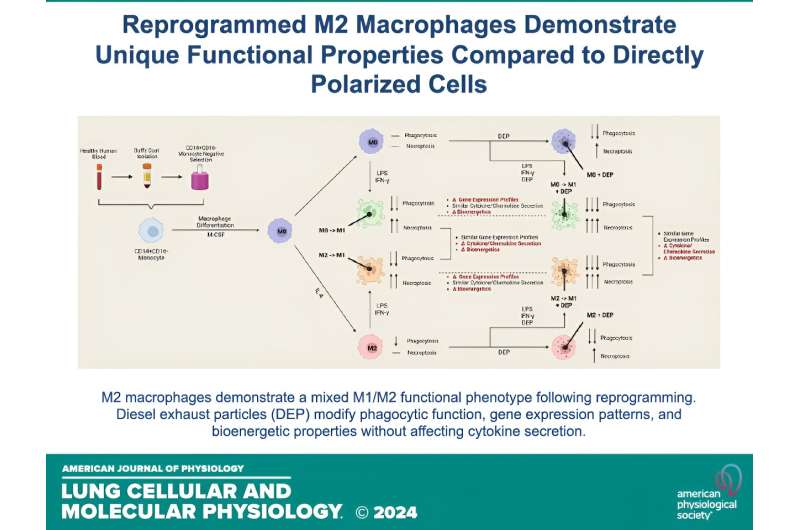
Credit: American Journal of Physiology- Cellular and Molecular Physiology of the Lung (2023). DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00085.2023
According to researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, exposure to diesel exhaust particles induces high levels of inflammation, particularly during respiratory infections. The researchers found that diesel exhaust blocks a process that boosts the immune response and alters the body’s protective response against tissue-damaging immune cells.
In addition, their findings suggest that exposure to exhaust particles may lead to increased inflammation in the lungs. the study Published in American Journal of Physiology- Cellular and Molecular Physiology of the Lung. It has been selected as an APS Select Essay for February.
Research has long proven that air pollution has negative effects on human health. Diesel emissions are a common form of air pollution in industrialized communities. Short-term exposure to diesel exhaust can cause headaches, dizziness, and eye, nose, and throat irritation. Long-term exposure may increase the risk of lung cancer and cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and heart cancers. Respiratory diseases.
The purpose of this study was to investigate whether diesel exhaust particles, a component of air pollution, induce changes in immune cells. The researchers wanted to examine how air pollution particles alter the ability of these immune cells to reprogram, which is necessary to enhance the host’s response to infection.
The researchers collected blood from healthy people and isolated monocytes, a type of white blood cell involved in the immune response, which develop into macrophages. The resulting monocyte-derived Immune cells exposed to various stimuli such as cytokines. This caused the cells to transform into different macrophage types.
After stimulation, the researchers measured immune cell function to assess their ability to capture bacteria, energy-generating properties and biomarkers of inflammation. They found a decrease in the ability to capture bacteria and an increase in biomarkers of inflammation.
“Exposure to Air pollution Normally associated with error Health outcomes“, said Ilona Jaspers, Ph.D., lead author of the study, and professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
“These findings may direct further research into this unique macrophage population, introducing new therapeutic pathways to ensure proper macrophage function that will in turn improve immune responses and reduce disease severity.” will.”
More information:
Timothy Smyth et al, Diesel exhaust particles induce polarization state-dependent functional and transcriptional changes in human monocyte-derived macrophages, American Journal of Physiology- Cellular and Molecular Physiology of the Lung (2023). DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00085.2023
Provided by
American Physiological Society
Reference: Diesel exhaust can damage immune system, trigger inflammation (2024, Feb 21) https://phys.org/news/2024-02-diesel-exhaust-immune-trigger- 21 Feb 2024 Retrieved from inflammation.html
This document is subject to copyright. No part may be reproduced without written permission, except for any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research. The content is provided for informational purposes only.
[ad_2]


