
[ad_1]
Super storm, sudden change in climate and New York City frozen in snow. Thus the blockbuster Hollywood film”The day after tomorrow“The sudden cessation of the Atlantic circulation and the disastrous consequences are shown.
While Hollywood’s approach was over the top, the 2004 film raised a serious question: If Global Warming If the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation shuts down, which is critical for transporting heat from tropical to northern latitudes, how sudden and severe will climate change be?
Twenty years after the film’s release, we know a lot more about the Atlantic circulation. Equipment installed at sea starting in 2004 Obviously the Atlantic circulation Is Clearly lazy Over the past two decades, possibly his The weakest state in nearly a thousand years. Studies also suggest that circulation has reached a A dangerous tipping point I Past Which sent him into a precipitous, unstoppable decline, and that May hit that tipping point again. As the planet warms and glaciers and ice sheets melt.
In a new study using the latest generation of Earth climate models, we simulated the flow of fresh water until ocean circulation reaches this tipping point.
The results show that circulation can Completely closed within a century of hitting the tipping point, and moving towards it. If so Average temperature Parts of North America, Asia, and Europe will drop by several degrees, and people will see severe and severe consequences all over the world.
We’ve also discovered a physics-based early warning signal that could warn the world when the Atlantic circulation is nearing its tipping point.
The conveyor belt of the ocean
Ocean currents are driven by winds, waves and water. Density differences.
In the Atlantic circulation, relatively warm and salty surface water near the equator flows toward Greenland. During its journey it crosses the Caribbean Sea, enters the Gulf of Mexico, and then flows along the US East Coast before crossing the Atlantic Ocean.
This current, also known as the Gulf Stream, brings heat to Europe. As it flows north and cools, the water mass becomes heavier. When it reaches Greenland, it begins to sink and begins to flow south. Sinking water near Greenland draws water from elsewhere in the Atlantic and repeats the cycle, e.g. Conveyor belt.
A lot of fresh water Melting glaciers and the Greenland ice sheet can dilute the salinity of water, prevent it from sinking, and weaken it. Sea conveyor belt. Oh Weak conveyor belts transporting Less heat to the north and also enables less heavy water to reach Greenland, which becomes weaker Conveyor belt power. Once it arrives. The tipping pointit closes quickly.
What happens to the climate at the tipping point?
The tipping point was first observed in an oversimplified model of the Atlantic circulation. Early 1960s. More today Detailed climate models Indicate continue. Deceleration of conveyor belt power Under the Climate change. However, the abrupt cessation of Atlantic circulation It seemed absent in them Climate models.
This is where our study comes in. We conducted an experiment with a detailed climate model to simulate a sudden shutdown by gradually increasing freshwater input.
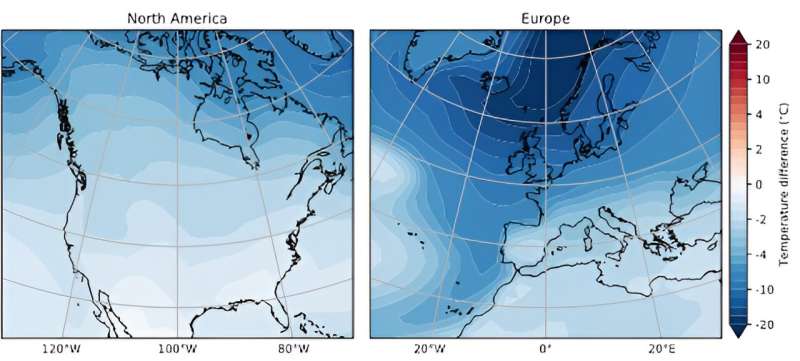
The change in annual mean temperature after the conveyor belt stopped shows extreme temperature reductions, especially in northern Europe. Renee M. van Westen
We found that once this tipping point is reached, the conveyor belt stops within 100 years. The northward heat transport is strongly reduced, causing an abrupt change in climate.
The result: dangerously cold in the north
Areas affected by the Gulf Stream. Low enough heat When circulation stops. It cools the North American and European continents by a few degrees.
The European climate is much more influenced by the Gulf Stream than in other regions. In our experiment, this meant that parts of the continent changed by more than 5 degrees Fahrenheit (3 degrees Celsius) per decade—much more than today’s global warming of about 0.36 degrees Fahrenheit (0.2 degrees Celsius) per decade. We learned that some parts of Norway would experience Decrease in temperature Above 36 F (20 C), on the other hand, Southern Hemisphere regions will warm by a few degrees.
These temperature changes develop over about 100 years. It seems a long time, but on the time scale of normal climate, it is sudden.
Conveyor belt closures will also affect sea level and rainfall patterns, which may occur. Push other ecosystems closer to their tipping points.. For example, the Amazon rainforest is endangered. Decrease in rainfall. If its forest ecosystem changes to grassland, there will be a transition. Release carbon into the atmosphere and results in the loss of a valuable carbon sink, further accelerating climate change.
There is the circulation of the Atlantic Ocean. Significantly slower in the distant past. During Ice ages As the ice sheets covering large parts of the planet were melting, the influx of fresh water slowed the circulation of the Atlantic Ocean, triggering large climate fluctuations.
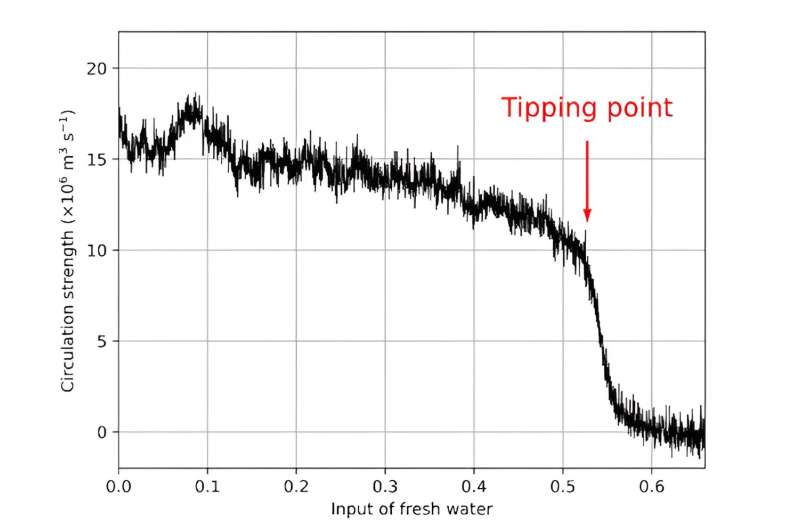
Climate model experiment shows how quickly the AMOC slows down after reaching a tipping point with a threshold of fresh water entering the ocean. How soon that will happen is an open question. Credit: Renee M. van Westen
So, when will we see this tipping point?
The big question — how long will the Atlantic circulation reach — remains unanswered. Observations do not go back far enough to provide a clear conclusion. While a recent study suggested that the conveyor belt is faster Near its tipping pointPossibly within a few years, these statistical analyzes made several assumptions that introduced uncertainty.
Instead, we were able to develop a physics-based and observable early warning signal involving the transport of salinity across the southern boundary of the Atlantic Ocean. Once a threshold is reached, a tipping point is likely to follow in one to four decades.
Our study illustrates the impact of climate on the magnitude of such sudden conveyor belt collapses. Changes in temperature, sea level and rainfall will adversely affect society. Climate change is unstoppable. On a human time scale
It may seem counterintuitive to worry about extreme cold as the planet warms, but if the main circulation of the Atlantic Ocean is shut down by the outflow of too much meltwater, the threat lies ahead.
Provided by
Conversation
This article has been republished. Conversation Under Creative Commons License. read Original article.![]()
Reference: Once Melting Glaciers Shut Down Gulf Stream, We’ll See Extreme Climate Change Within Decades, Study Shows (2024, Feb. 17) Accessed February 17, 2024 at https://phys.org/news/2024-02- Retrieved from glaciers-gulf-stream-extreme-climate.html
This document is subject to copyright. No part may be reproduced without written permission, except for any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research. The content is provided for informational purposes only.
[ad_2]


